Refrigerated Containers (Reefer Containers)
Refrigerated containers, also known as reefers, are airtight containers used to transport goods that require a controlled temperature, such as fresh fish, meat, frozen foods, fruits, vegetables, film, and pharmaceuticals. There are three main types: refrigerated containers, reefer containers, and insulated containers.
Features of Refrigerated Containers:
- Material and Structure: These containers are made of galvanized steel with inner walls, floors, roofs, and doors constructed from composite metal panels, aluminum, stainless steel, or polyester.
- Standardization: International standards govern the size and performance of these containers.
- Temperature Range: The typical temperature range is from -30°C to 12°C, with a broader range of -30°C to 20°C for more versatile models.
Refrigerated containers offer the following advantages:
- Flexible loading and unloading
- Stable temperature control during transportation
- Minimal contamination and loss of goods
- Compatibility with various transportation modes
- Faster loading and unloading
- Shorter transit times
- Cost-efficient transportation
Reefer Containers
Reefer containers can adjust their internal temperature between -60°C and +30°C and are available in two types: built-in and external.
- Built-in Reefer Containers: Equipped with a refrigeration unit that can be activated during transit to maintain the required temperature.
- External Reefer Containers: Depend on specialized vehicles, ships, or terminals with refrigeration equipment to maintain the desired temperature.
These containers are ideal for transporting goods such as butter, chocolate, frozen fish and meat, condensed milk, and margarine, especially during summer.
Common Specifications for Refrigerated Containers
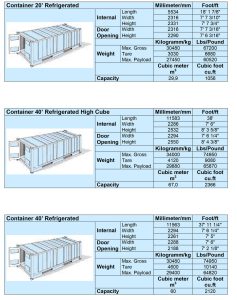
- 20-ft Reefer Container
- External Dimensions: 5.42×2.26×2.24m to 6.05×2.43×2.59m
- Internal Dimensions: 5.90×2.35×2.39m
- Capacity: 33.2 cubic meters
- Tare Weight: 2.23 tons
- Payload: 21.77 tons
- Gross Weight: 24 tons
- 40-ft Reefer Container
- External Dimensions: 12.2×2.4×2.59m
- Internal Dimensions: 11.2×2.24×2.18m to 12.0×2.3×2.39m
- Capacity: 67.7 cubic meters
- Tare Weight: 3.7 tons
- Payload: 26.78 tons
- Gross Weight: 30.48 tons
- 40-ft High Reefer Container
- Internal Dimensions: 11.62×2.29×2.50m
- Capacity: 67 cubic meters
- Payload: 22 tons
- 45-ft Reefer Container
- Internal Dimensions: 13.10×2.29×2.50m
- Capacity: 75 cubic meters
- Payload: 29 tons
Note: Slight variations may occur among containers from different shipping lines.
Important Considerations for Using Reefer Containers
- Quality Check: Inspect the original quality of refrigerated or frozen goods before loading and note the findings on the shipping document.
- Proper Stacking: Follow strict stacking principles to avoid cold air short-circuiting, which can lead to uneven cooling and reduced efficiency.
- Temperature Control:
- For frozen goods, the temperature deviation should not exceed ±3°C during long-distance transportation.
- For chilled goods, the deviation should be less than 0.5°C, ideally not exceeding 0.25°C.
- Ventilation:
- When transporting fresh fruits or vegetables, open the air vent for ventilation.
- For frozen goods, keep the air vent closed.
- Humidity Management: When transporting chilled goods in paper cartons, ventilate as necessary to keep the air dry and prevent condensation on the cartons.
- Pre-Cooling:
- Avoid pre-cooling the container as warm air entering upon opening can cause condensation, damaging the packaging and reducing refrigeration efficiency.
- Pre-cooling is permissible when the cold storage and container temperatures are the same, and cold air channels are used for loading.
- Pre-Cooling Goods: Pre-cool goods, wooden pallets, and other materials to the required temperature before loading, as reefer containers are designed to maintain temperature rather than cool goods from high temperatures.
- Loading Precautions:
- Set the correct temperature, airflow rate, and humidity before loading.
- Ensure the refrigeration unit is off during loading.
- Stack goods below the red load line and keep them within the vertical plane of the T-shaped floor grooves.
- Ensure goods are securely packed, and the total weight does not exceed the container’s payload limit.
- Transport Efficiency:
- For short distances (less than 3 hours), consider using regular vehicles to reduce costs.
- Schedule container pick-ups 1-2 days before the vessel’s departure to minimize storage costs at the port.
- Minimize Port Storage Costs: Quickly arrange delivery after the container arrives at the port to reduce plug-in fees for maintaining refrigeration.
By following these guidelines, reefer containers can effectively ensure the safe and efficient transport of temperature-sensitive goods.

