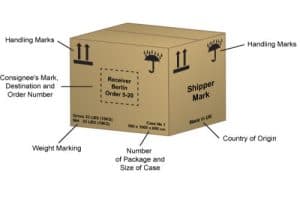
1. What Are “Shipping Marks”?
In international trade, the term “shipping mark” is commonly pronounced as “mài tóu” or “mà tóu” in Chinese, both derived from the English word “MARK.” As an essential transportation mark, shipping marks play a crucial role in foreign trade. The term “No Mark” is often abbreviated as “N/M” in practical business applications.
Shipping marks typically include the following information:
- Country or region code;
- Port of shipment and destination port;
- Shipper and consignee information;
- Product name, quantity, weight, and specifications;
- Order number;
- Country of origin;
- Special marks (e.g., fragile items, hazardous goods requiring special labeling);
- Other necessary identification details.
2. What Are the Functions of Shipping Marks?
- Facilitating Cargo Identification – When exporters load goods into containers, “shipping marks” are printed on the outer packaging to allow logistics personnel to quickly recognize and classify the cargo.
- Preventing Confusion or Misdelivery – Serving as the “ID card” of the cargo, shipping marks clearly indicate product names, specifications, and quantities, reducing the risk of misdelivery and ensuring that goods arrive safely at their destination.
- Enhancing Logistics Efficiency – Clear shipping marks help both shippers and carriers manage bulk cargo effectively. They also assist customs and inspection authorities in their regulatory tasks, improving overall trade efficiency.
3. How Are Shipping Marks Classified?
As an effective way to distinguish different goods, shipping marks can be categorized into the following types:
- Text-Based Marks – Clearly label cargo information using written text.
- Graphic-Based Marks – Utilize simple shapes like squares, triangles, and circles for quick recognition.
- Symbol-Based Marks – Use numbers and letters for concise identification.
Additionally, shipping marks can be divided into:
- Main Marks (Front Marks): Usually printed on the front of the carton, containing details like the shipper, consignee, order number, production batch number, and destination port.
- Side Marks: Printed on the sides of the carton, typically including product name, quantity, gross weight, net weight, and volume.
4. Key Considerations for Using Shipping Marks
- Clarity and Visibility – Shipping marks should be placed prominently on the packaging, using clear fonts and symbols that are waterproof and stain-resistant to maintain readability.
- Accuracy and Compliance – The information displayed on shipping marks must accurately reflect the cargo details and comply with the legal regulations of relevant countries.
- Standardization – Adopting a uniform format for shipping marks improves logistics efficiency and management.
Shipping marks are a fundamental aspect of international trade, ensuring the smooth identification, transportation, and customs clearance of goods while minimizing logistical risks.

